When I first met SSL, I was finding a way to keep my data secreted while it’s being transmitted between my server and iOS device. Then a mess of file types, such as .key .csr .crt .p12 .der .cer .pem, and the picture below just scared me. Why a data encryption tech need to be so complicated?
After reading lot of articles and posts, I finally get some clues.
Let’s start with a story about Harry wanna send a mail to Sirius through Internet. Umbridge, a super hacker for whom Internet is totally transparent, trys to intercept.
Master Secret (MS)
When somebody wants to send others a secretive message, the first thing comes to him maybe is to encrypt the message. To achieve this, we need a pair of encrypt/decrypt methods and a secret. The message can only be decrypted using the same secret which was used to encrypt it. The diagram should be as simple as:
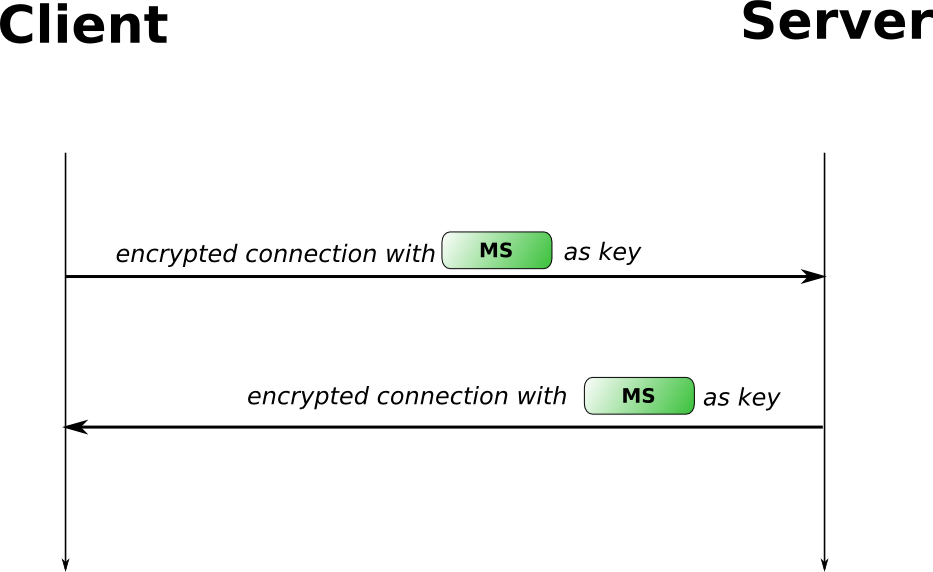
This is a good idea, but not works in our story. Because Harry can’t meet Sirius, so that he has to send the secret through Internet too, just like he sends the message itself. We already know everything exposed on Internet can be catched by Umbridge. Since there are only a few encrypt/decrypt methods and they are all well known, Umbridge can decrypt and read the message.
To deal this problem, some wise men invented Asymmetric Cryptography
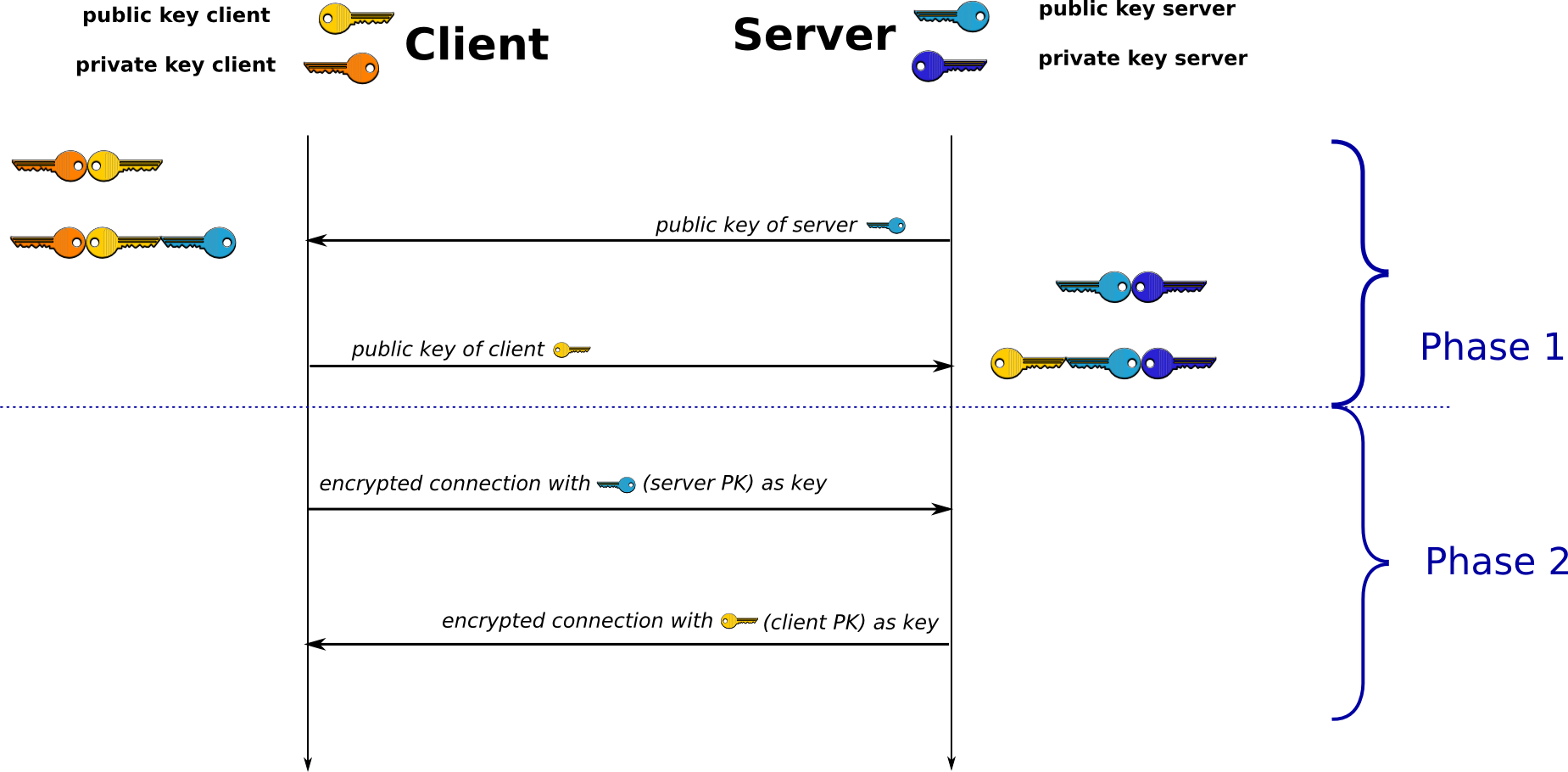
Asymmetric Cryptography
One main difference between Asymmetric Cryptography and traditional cryptograghy (also named Reciprocal Cipher) is that the former has two secrets. And if you get something encrypted with SECRET-A, you can’t decrypt it unless you have SECRET-B.
The two secrets are well known as public-key and private-key. The relationship between them is like left and right. Left is so called left is baecause the other side is called right. If you choose public-key as private-key, the private-key can be used as public-key too. And in fact we did use them that way.
So, with this fantanstic algorithm. Harry and Sirius both have a pair of keys, firstly they send their public-key to each other openly. Secondly, they encrypt the message with each other’s public-key they just received. And their private-keys, of course, they will keep them private. Without exposed private-key, Umbridge is not able to decrypt their message.
The connection encrypted with Asymmetric Cryptography is like this:
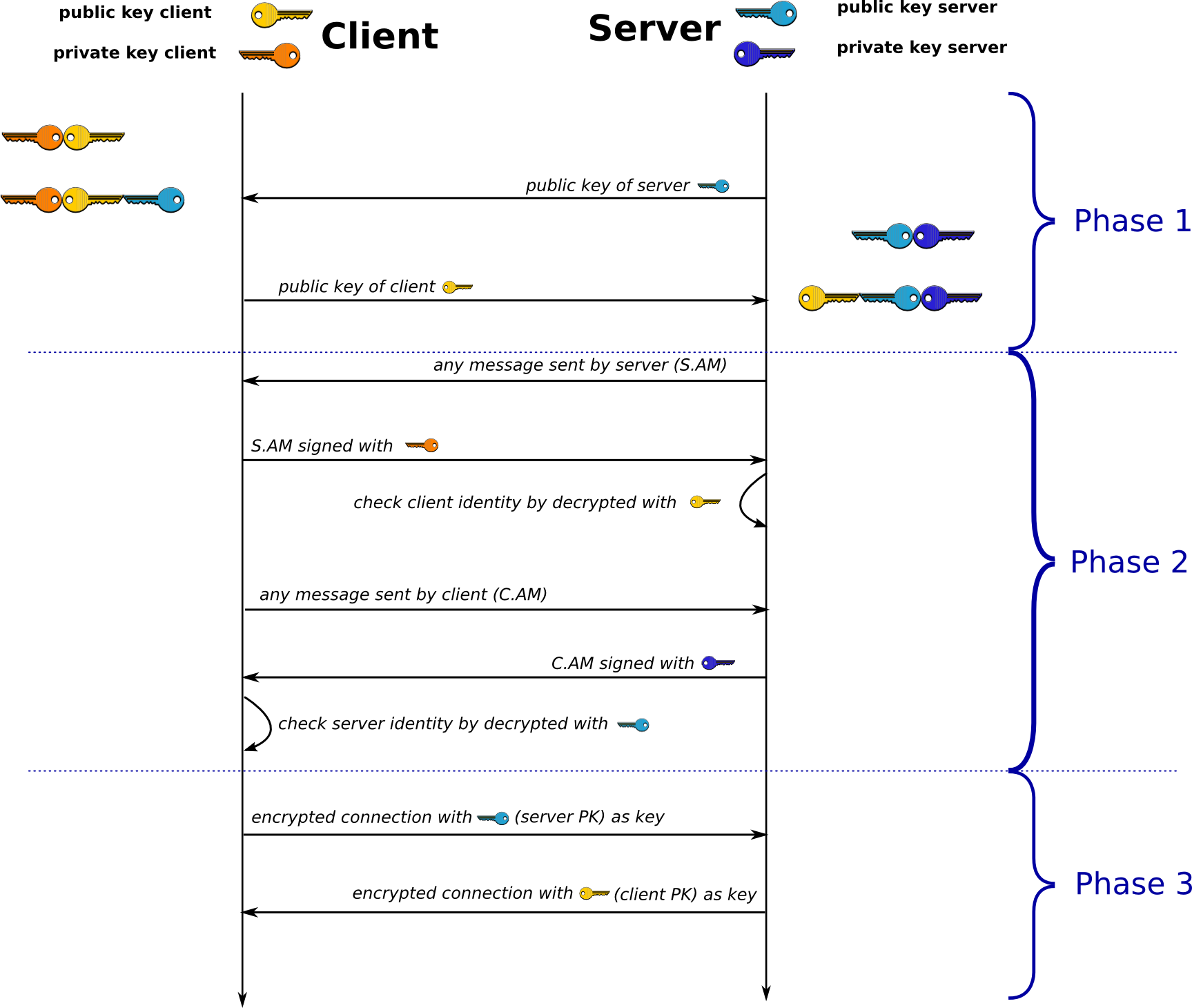
Digital Signature
Umbridge is full of craft and cunning. She disguises herself as Sirius, and sends Harry her public-key. Harry is so naive that he encrypt the message with Umbridge’s public-key and send it out. When Harry and Sirius both find out the fact it was too late, but they still need a way to avoid this kind of attack to happen again.
This kind of attack is well known as Man-in-the-middle attack (MITM). People have invented a way named Digital Signature to avoid it. It is simple. Usually we use each other’s public-key to encrypt message, when do Digital Signature we just use our own private-key to encrypt. And the encrypted message can be decrypted with our own public-key only. What is interesting is you do not need to care what the message is, you just decrypt it and make sure that is exactly same with the message you sent me, then it can prove the message sender is definitely me.
Add Digital Signature to the diagram
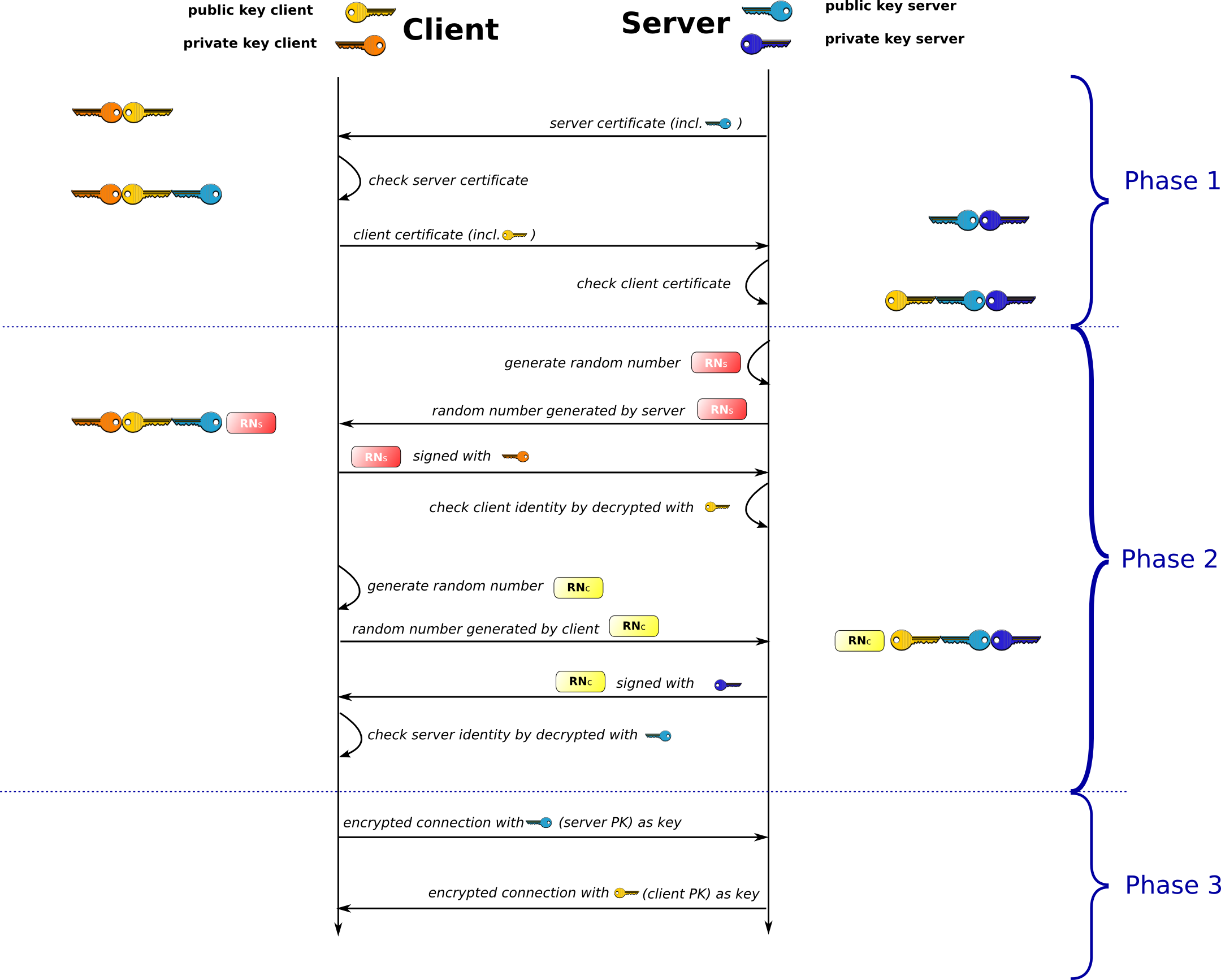
Random Number
Umbridge gets something new once more. She catched some message, although she wasn’t able to decrypt it, she found they were all same. This means lazy Harry send same message to Sirius and let him do Digitial Signature. When Sirius sends signed message back, Harry succesfully decrypts it with Sirius’s public-key, and believe the one on the other side is surely Sirius. Umbridge used Harry’s laziness, and waited for Harry sending out the old message, she sent back Harry the message she catched early (but unable to decrypt). Harry decrypt it once more, and fooled by Umbridge once more.
Sirius is annoyed about that. He told Harry to never use the same authentication messge, they need Random Number. OK, there isn’t real random in computer’s world. The key here is when Umbridge send back an old mock authentication message, Harry will recognize it’s not same with the one he just sent out.
Use Random Number as authentication message

Certificate
Using the methods mentioned above, we can ensure the messages are safe while being transmitted. But we can’t avoid to communite with stangers in the real life. How can we make sure who is trustable and who is not?
Here has to be the forth people, Regulus, Sirius’ brother. He wants to communicate with Harry via Internet too. But Harry doesn’t know him. So Regulus wrote in his message, “I’m a brother of Sirius”, and he sent the message to Sirius. Sirius did Digital Signature on the message and send it back. Next time when Regulus wants to write to Harry He just needs to embed this message in the mail, Harry will know it’s Regulus someone believable and certificated by Sirius.
The relationship message signed by Sirius is called certificate, consists of Trust Train and the owner’s public-key, and it is signed (digital) by Certificate Authority (CA, Sirius here). The existence of a note in the Trust Chain indicates it is trusted by the CA. And the taker can use the public-key to verify if it is truly the one in the chain.
Performance
After go this far, we get all we need to make our connection safe. But the diagram still does not look like the one from wikipedia. I believe it is because there are some alterations to improve the performance:
- Asymmetric Cryptography is safer but costs more time than traditional encryption. The good and fast way is to
use Asymmetric Cryptography to generate amaster-secret, then usemaster-secretto encrypt the following communication. - In the real scene, server always service huge amount of clients. Therefore it would be better if the client can affort more operation during a SSL handshake. For instance, 1) client should start the handshake, 2) client will do the Digital Signature, 3) client will generate the pre-master-secret, 4) client will do the only encryption using Asymmetric Cryptography, 5) server can choose not to check the identity of client
Consider factors above the diagram will look like this:

Negotiate
SSL has been born and improved for years. During these time, many different encryption algorithm and versions and standards have been imported. So server and client will negotiate and choose the highest version they both support to make the communication as safe as they can. That is the last thing we don’t have in the diagram.
Files
Basiclly files with different different extensions have different encodings or structures, but all consists of concepts above. I found an excellent blog to describe it, DER vs. CRT vs. CER vs. PEM Certificates.
As supplementary, the ‘r’ in the extension .csr indicates ‘request’. If you have a .key file, you can use openssl to generate a .csr file with it. Then CA will generate a certificatei (.cer or .crt or something equal) according to the .csr file.
