The three parameters primaryjoin, secondary, secondaryjoin of function relationship() are the keys of many to many relationship.
In SQL, to impletement Many-to-Many requires three tables. Let’s call them Table A, B, C. Table A and B for two entities need to be related, and table C present the relationship.
Back to our three parameters of relationship(). Parameter secondary is the table C, primaryjoin is the method that connects C and A (or B), secondaryjoin is another method that connects C and B (or A).
For instance, the code may look like this:
attend_party = Table('attend_party',
Column('people_id', Integer, ForeignKey('people.id')),
Column('party_id', Integer, ForeignKey('party.id'))
)
class People(Base):
__tablename__ = 'people'
id = Column(
Integer, primary_key=True
)
class Party(Base):
__tablename__ = 'party'
id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
participant = relationship(
'People',
primaryjoin= lambda : Party.id==attend_party.c.party_id,
secondary=attend_party,
secondaryjoin= lambda : attend_party.c.people_id==People.id,
backref=backref('parties_attended')
)
And I make a diagram:
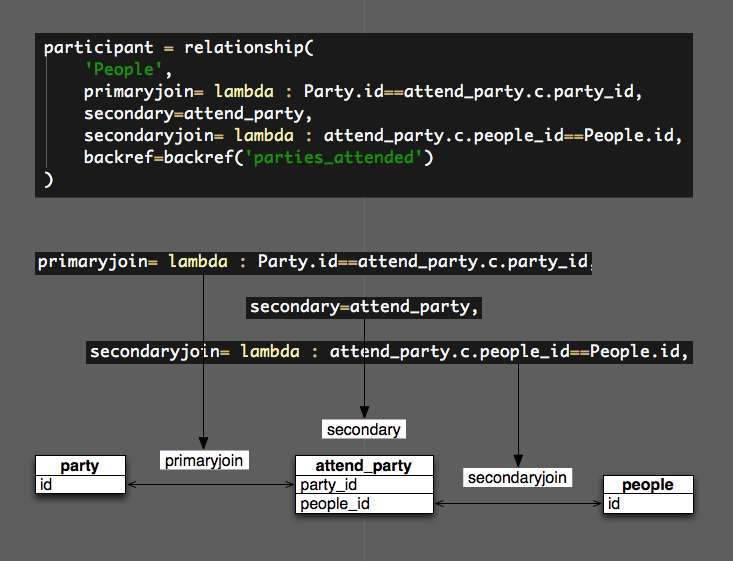
Finally thanks to the fuction ForeignKey(), it bounds the two columns that need to be joined (primary or secondary). In the sample above, the property participant of class Party can be simplified like this:
participant = relationship(
'People',
secondary=attend_party,
backref=backref('parties_attended')
)
Simple is the best!